Introduction:
The Social Security Number (SSN) has become an integral part of modern life, serving as a unique identifier for millions of individuals in the United States. Originally introduced in 1936 as a tool to track workers’ earnings and administer social security benefits, the SSN has evolved into a multifaceted identification system with far-reaching implications. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Social Security fullz info, exploring their history, structure, uses, and the importance of safeguarding this sensitive information.
History and Purpose:
The origins of the Social Security Number can be traced back to the Social Security Act of 1935, during the Great Depression. The primary objective was to establish a system of social insurance that would provide economic security for retirees and the unemployed. The SSN was introduced as a means to accurately record workers’ earnings and administer benefits.
Structure of Social Security Numbers:
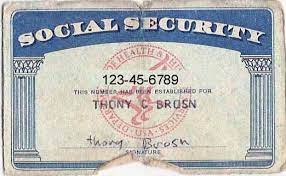
A Social Security Number is a nine-digit identifier, typically presented in the format XXX-XX-XXXX. The numbers are not randomly assigned; instead, they follow a specific pattern. The first three digits, known as the Area Number, were originally assigned based on the geographical location of the applicant’s residence. The next two digits, the Group Number, were used for internal purposes, and the last four digits, the Serial Number, were assigned sequentially.
However, changes in the assignment process over the years have made it challenging to deduce an individual’s location from the Area Number alone. Today, SSNs are primarily issued based on the Zip Code of the mailing address provided during the application.
Uses of Social Security Numbers:
Over the years, the use of Social Security Numbers has expanded beyond its original purpose. While it remains a crucial element for administering social security benefits, it has also become a widely accepted form of identification. SSNs are required for various financial transactions, employment verification, tax reporting, and even when applying for government benefits.
Protecting Your Social Security Number:
Given the extensive use of Social Security Numbers, protecting this sensitive information is paramount. Identity theft and fraudulent activities are serious concerns associated with the compromise of SSNs. Individuals are advised to be vigilant about sharing their SSN and to provide it only when absolutely necessary. Additionally, monitoring credit reports regularly can help detect any suspicious activities linked to the SSN.
Legislation and Initiatives:
Recognizing the need for enhanced protection of SSNs, legislative measures have been enacted to safeguard individuals’ personal information. The Social Security Number Protection Act of 2019, for example, aims to restrict the unnecessary collection, display, and dissemination of SSNs.
Conclusion:
The Social Security Number has come a long way since its inception, evolving from a tool to administer social security benefits to a ubiquitous identifier in various aspects of life. Understanding its history, structure, and the importance of safeguarding this sensitive information is crucial for individuals to navigate the complexities of modern society. As we continue to rely on SSNs for identification purposes, it is essential to strike a balance between convenience and security to protect ourselves from potential risks and ensure the longevity of this vital identification system.